Define the term mutation
Is a sudden change in the genetic make up of an individual
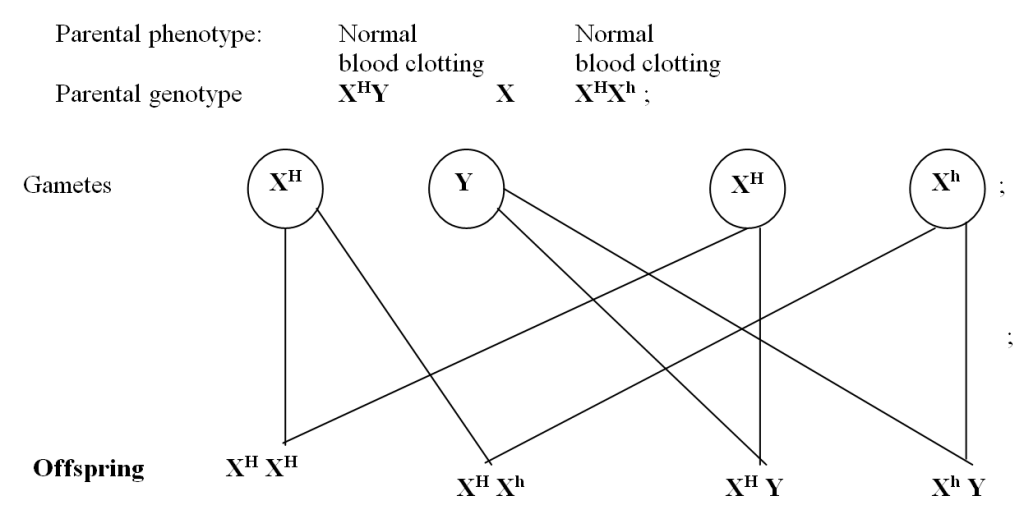
A couple, George and Grace had a son who was suffering from haemophilia even though none of them
showed signs of haemophilia.
i) State the genotype of George and Grace.
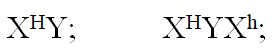
Using a genetic cross work out the genotype of the couple’s son.
What are linked genes?
Genes located on the same chromosome and are transmitted together;
An experiment was set up to investigate the effect of unilateral light on the growth of oat coleoptile. The diagrams in the table below represent the experimental set ups at the start, and at the end of the experiment.
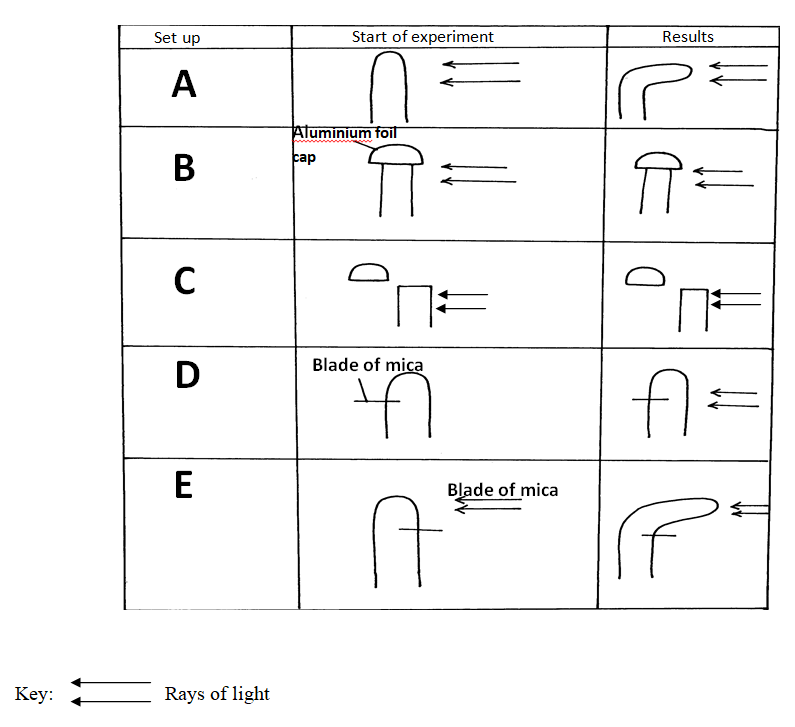
a) Account for the results in the experimental setup A.
The coleoptile tip bends towards light/positive phototropism/positively phototropic; more cells elongating/more growth on the side away from light; due to high auxin concentration on the side away from light;
b) Explain the purpose of experimental set ups B and C.
B and C are control experimental set ups for A;
B shows that it is the tip that responds to light
C shows that it is the tip of that is the source of growth hormones/auxins/1AA;
c) Explain the results in experimental set ups D and E.
No curvature in D because hormones/Auxins/1AA from the tip do not reach region of cell elongation (due to mica blade); in E curvature occurred because mica blade does not interfere with the tip to region of cell elongation on the side away from light;
Three pieces of potato cylinders of equal length were placed in three solutions of different concentrations. The set ups were left to stand for 45 minutes. The results were recorded in the table below.
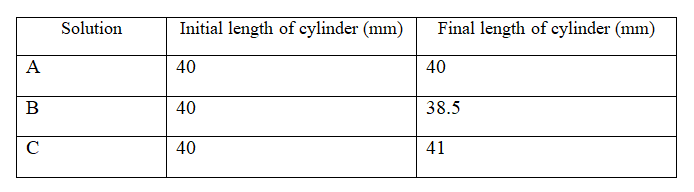
a) Describe the nature of solution A in relation to the concentration of the potato cells.
Isotonic solution;
b) Explain the observation that was made on the potato cylinder which was put in solution B.
Solution B was hypertonic; to potato cells. The cells lost water to solution B through osmosis; and became plasmolysed hence the reduction in length of the cylinder;
c) i) State what would happen to red blood cells if they were placed in solution C.
The cell would be haemolysed; cells would burst
ii) Explain your answer in (c)(i) above.
The solution is hypotonic to red blood cells; the cells would gain water by osmosis then swell and burst;
d) Name the process involved in uptake of mineral salts by plants from the soil.
Active transport;
a) Explain the term double fertilization as applied in plants.
One male nucleus of the pollen grain fuse with the polar nuclei; to from triploid primary endosperm nucleus; while the other male nucleus fuse with the egg cell nucleus; to form the zygote; (that develop into embryo)
b) State the role of each of the following hormones in male humans.
i) Follicle stimulating hormone.
Stimulates the synthesis/maturation of sperms;
ii) Testosterone
Stimulates the development of secondary male characteristics;
c) What is in vitro fertilization?
Fertilization of ovum is done in a test tube; and the fertilized ovum is transferred into mother’s uterus;
d) Name the causative agent of gonorrhea.
Neisseria gonorrhea;
The diagram below shows part of gaseous exchange system in an insect. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
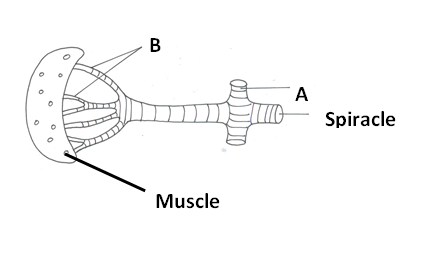
a) What are the structural adaptations of the parts labelled A and B to their functions?
i) A has a Presence of rings of chitin which keeps them always open ;
ii) B has Moist epithelium for dissolution of respiratory gases;
b) Name the parts of the following animals that carry out the same function as part B above. (2mks)
i) Man…
ii) Tilapia fish……
i) alveoli;
ii) gill filaments
c) Name the structures used for gaseous exchange in plants growing in water logged soils.
pneumatophores;
d) i) Give two reasons why accumulation of lactic acid during vigorous exercise leads to an increase in heartbeat.
Lactic acid is poisonous to tissues and must be removed; to increase supply of oxygen to tissues;
ii) In what form is oxygen transported from lungs to the tissues?
Oxyhaemoglobin; Accept: HbO2/HbO8
During germination and growth of a cereal, the dry weight of the endosperm, the embryo and total dry weight were determined at two day intervals. The results are shown in the table below.
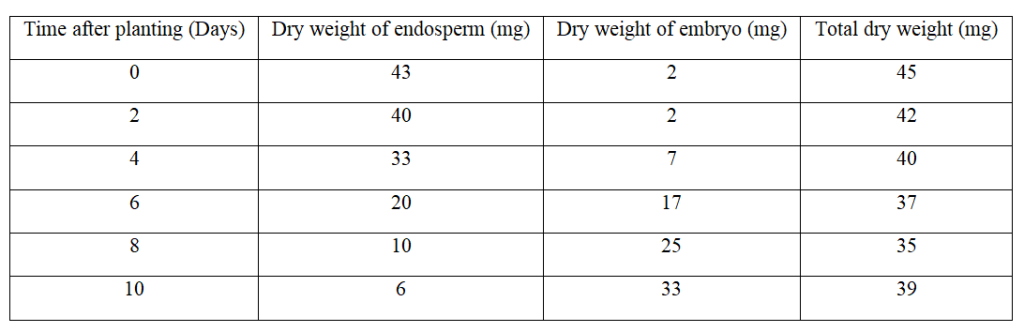
a) On the same axes, draw graphs of dry weight of endosperm, embryo and the total dry weight against time.
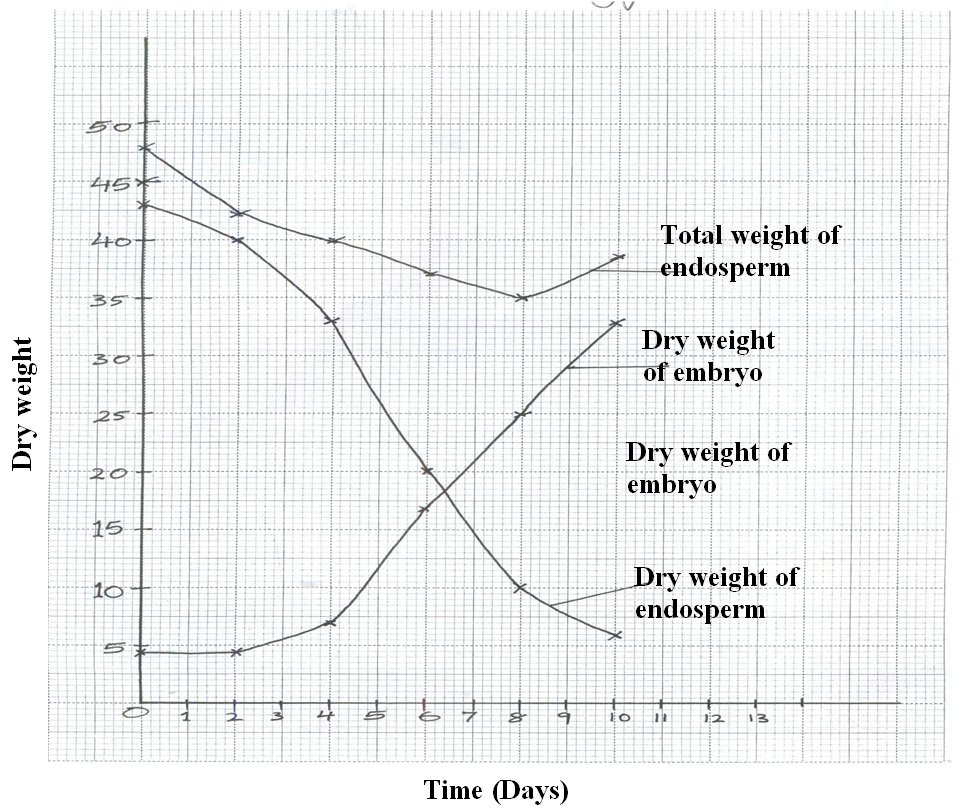
b) What was the total dry weight on day 5?
38.5mg; ± 0.5 Reject: wrong units , Accept: without units
c) Account for:
i) Decrease in dry weight of endosperm from day 0 to day 10.
Hydrolysis of starch into simple sugar/glucose; which is translocated to the embryo; oxidation (of simple sugars) respiration to carbon (iv) oxide/energy/Heat
ii) Increase in dry weight of embryo from day 0 to day 10.
New cells materials/tissue are synthesized (from proteins); bringing about growth of embryo;
iii) Decrease in total dry weight from day 0 to day 8.
First leaf carried out photosynthesis (Leading to growth)
iv) Increase in dry weight after day 8.
d) State two factors within the seed and two outside the seed that cause dormancy.
i) Factors within the seed
i) presence of absiscic acid; Acc presence of germination inhibitors.
Embryo not fully developed;
Absence of hormones/enzymes that stimulate germination; impermeable seed coat; (Any two)
ii) Factors outside the seed
Unsuitable temperature/lack of suitable temp/ unfavourable temperature;
Lack of water;
Absence of light;
Lack of Oxygen;
e) Give two characteristics of meristematic cells
- Dense cytoplasm;
- Thin cell wall
- absence of vacuoles
- 12 Tips for Studying Biology EffectivelyStudying biology can be an exciting and rewarding endeavor. Here are some steps and tips to help you study biology effectively: Remember, studying biology is a gradual process, and it’s important to stay consistent and patient. By following these steps and adopting effective study habits, you can develop a strong foundation in biology and unlock… Read more: 12 Tips for Studying Biology Effectively
- 2014 KCSE Exam For Biology Paper 2Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 64 Related posts: Causes of Disunity in the Early Church HOMESCIENCE PAPER 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004 APPROACHES TO LAW, ORDER AND JUSTICE BIOLOGY PAPER 3 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.PDF The diagram below shows the position of an image formed in… Read more: 2014 KCSE Exam For Biology Paper 2
- 2014 KCSE Exam For Biology Paper 3Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 54 Related posts: KCSE BIOLOGY PAPER 3 MOCKS MODEL08052023008 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.PDF The diagram below shows the position of an image formed in a defective eye Explain continental drift as an evidence of evolution A certain animal… Read more: 2014 KCSE Exam For Biology Paper 3
- A certain animal has no incisors, no canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars in its upper jaw. It has 6 incisors, 2 canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars on the lower jaw. Write its dental formulab) State the likely mode of feeding for the animal Herbivorous c) Give a reason for your answer in (b) above Lack of canines/incisors on the on the lower jaw/presence of canines / Incisors on the lower jaw only Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 157 Related… Read more: A certain animal has no incisors, no canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars in its upper jaw. It has 6 incisors, 2 canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars on the lower jaw. Write its dental formula
- A group of students from Awasi Boys High School set up an experiment to demonstrate a certain process. The experimental set up were as shown in the diagrams below.A group of students from Awasi Boys High School set up an experiment to demonstrate a certain process. The experimental set up were as shown in the diagrams below. After 10 minutes the students recorded their observation in a table as shown below. a) Name the process being demonstrated by this experiment. (1mk) Diffusionb) Explain… Read more: A group of students from Awasi Boys High School set up an experiment to demonstrate a certain process. The experimental set up were as shown in the diagrams below.
- A set up that was used to investigate a certain process in plants as shown in the diagram below.a) What process was being investigated? (Rate of) transpiration b) i) State two precautions that should be taken when setting up the experiment. Cut shoot under water Apply petroleum jelly to cork-glass/Bung-glass/Bung-shoot connection Open reservoir tap ii) Give a reason for each precaution stated in b(i) above. To ensure no air enters leafy shoot/xylem To… Read more: A set up that was used to investigate a certain process in plants as shown in the diagram below.
- A substance which accumulates in muscles when respiration occurs with insufficient oxygenDiscover how lactic acid builds up in muscles during oxygen-deprived respiration and its effects on the body. Explore the consequences of oxygen debt and strategies to alleviate muscle fatigue.
- Ace the KCSE Biology Exam with Free KNEC Based Papers and Marking SchemesReview of Free KNEC KCSE-Based Biology Papers with Marking Schemes Are you in search of comprehensive and reliable resources to prepare for the KCSE Biology exam? Look no further than swalijibu.co.ke and Atika School, where you can download free KNEC KCSE based Biology paper 1, 2, and 3 questions with marking schemes since 1995! These… Read more: Ace the KCSE Biology Exam with Free KNEC Based Papers and Marking Schemes
- BIOLOGY FORM 3 TERM 2 PAPER 1 AND 2 QUESTION PAPER MODEL1682022001PAPER 1 PAPER 2 TO GET MARKING SCHEMES ON WHATSAPP SEND KSH 50/= TO BUY GOODS AND SERVICES TILL 5151451 THEN SMS MODEL1682022001 Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 878 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH… Read more: BIOLOGY FORM 3 TERM 2 PAPER 1 AND 2 QUESTION PAPER MODEL1682022001
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 NOTES MODEL28082022001Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 99 Related posts: KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES BIOLOGY PAPER 3 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.PDF FORM 2 TERM 1 BIOLOGY REVISION PAPER MODEL15082023001 The diagram below shows the position of an image formed in a defective eye Explain continental… Read more: BIOLOGY FORM 4 NOTES MODEL28082022001
- BIOLOGY GRAPHICAL QUESTIONSBIOLOGY GRAPHICAL QUESTIONS Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 120 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES The diagram below shows the position of an image formed in a defective eye Explain… Read more: BIOLOGY GRAPHICAL QUESTIONS
- Biology Paper 1 2022 K.C.S.E Prediction Set 1 MODEL20082023001Biology Paper 1 2022 K.C.S.E Prediction Set 1 Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 124 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES FORM 4 AGRICULTURE PAPER 1 AND 2 REVISION KITS IN… Read more: Biology Paper 1 2022 K.C.S.E Prediction Set 1 MODEL20082023001
- BIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME MODEL27082023015BIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME MARKING SCHEME Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 250 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES FORM 4 AGRICULTURE PAPER… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME MODEL27082023015
- BIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 4 QUESTION PAPER WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL2492017.pdfBIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 4 QUESTION PAPER WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL2492017.pdf Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 231 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE BIOLOGY PAPER 3 FORM 4 REVISION KIT 2023 MODEL2492017 KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 4 QUESTION PAPER WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL2492017.pdf
- BIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 4 TERM 2 EXAMS WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL24082023001.pdfBIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 4 TERM 2 EXAMS WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL24082023001.pdf Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 191 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES COMPUTER-STUDIES-FORM-2-TERM-2-EXAMS-MODEL21072023004-QUESTION-PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME FORM 4… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 4 TERM 2 EXAMS WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL24082023001.pdf
- BIOLOGY PAPER 1 QUESTIONS and ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.pdfBIOLOGY PAPER 1 QUESTIONS and ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.pdf Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 789 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS BIOLOGY PAPER 3 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.PDF HISTORY AND GOVERNMENT REVISION KIT WITH QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS FOR… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 1 QUESTIONS and ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.pdf
- BIOLOGY PAPER 2 – 2022 KCSE PREDICTION SET 1 MODEL20082023001BIOLOGY PAPER 2 – 2022 KCSE PREDICTION SET 1 Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 231 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES FORM 4 AGRICULTURE PAPER 1 AND 2 REVISION KITS… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 2 – 2022 KCSE PREDICTION SET 1 MODEL20082023001
- BIOLOGY PAPER 2 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME MODEL27082023015BIOLOGY PAPER 2 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME MARKING SCHEME Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 220 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES FORM 4 AGRICULTURE PAPER… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 2 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME MODEL27082023015
- BIOLOGY PAPER 2 FORM 4 QUESTION PAPER WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL2492017.pdfBIOLOGY PAPER 2 FORM 4 QUESTION PAPER WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL2492017.pdf Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 268 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE BIOLOGY PAPER 3 FORM 4 REVISION KIT 2023 MODEL2492017 KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 2 FORM 4 QUESTION PAPER WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL2492017.pdf
- BIOLOGY PAPER 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.pdfBIOLOGY PAPER 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.pdf Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 398 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS BIOLOGY PAPER 3 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.PDF BIOLOGY PAPER 1 QUESTIONS and ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.pdf HISTORY AND GOVERNMENT… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS MODEL20012023004.pdf
- BIOLOGY PAPER 3 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME MODEL27082023015BIOLOGY PAPER 3 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME QUESTION PAPER MARKING SCHEME Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 444 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES FORM 4… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 3 FORM 3 TERM 3 QUESTION PAPER AND MARKING SCHEME MODEL27082023015
- BIOLOGY PAPER 3 FORM 4 TERM 2 EXAMS WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL24082023001.pdfBIOLOGY PAPER 1 FORM 4 TERM 2 EXAMS WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL24082023001.pdf Tell your Besties … Facebook Twitter Linkedin Tumblr Reddit Pinterest Whatsapp Telegram Post Views: 167 Related posts: KCSE PAST PAPERS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 AND 3 QUESTIONS, ANSWERS-MARKING SCHEMES AND REPORTS KCSE ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND LITERATURE NOTES FORM 2 TERM 1 CHEMISTRY REVISION… Read more: BIOLOGY PAPER 3 FORM 4 TERM 2 EXAMS WITH MARKING SCHEME MODEL24082023001.pdf
