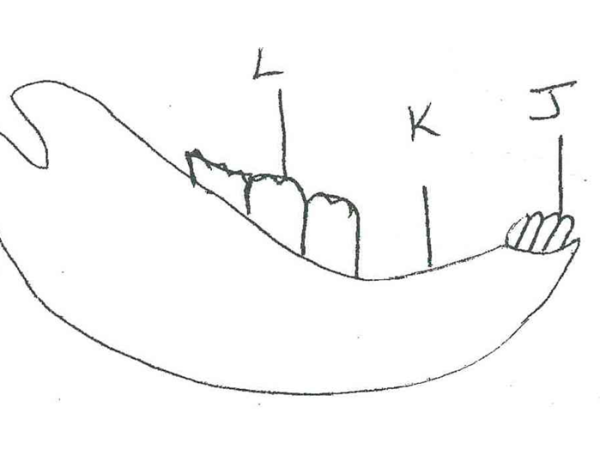
The diagram below represents the lower jaw of a mammal
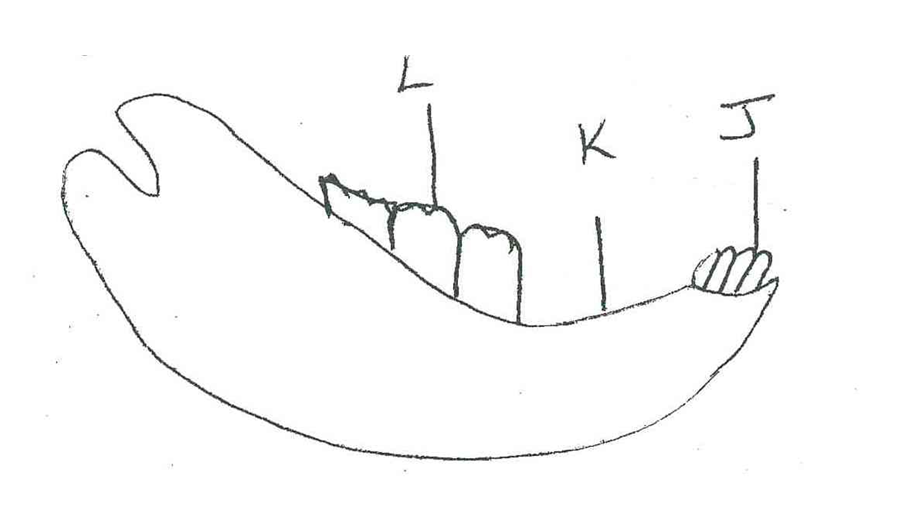
Name the mode of nutrition of the mammal whose jaw is shown. (1mk)
Holozoic Nutrition.
Give reason for your answer in (a) above. (1mk)
-Presence of teeth- shows feeds on solids.
State one structural and one functional difference between the teeth labeled J and L. (2mks)
J
Sharp edge
One root
L
Wide flat surface
Three roots.
i) Name the toothless gap labeled K. (1mk)
diastema
State the function of the gap.
Allows the tongue space for turning and moving food materials.
Name the substance that is responsible for hardening of teeth. (1mk)
Enamel
Name two dental hygiene practices. (2mks)
- Regular brushing of teeth after every meal.
- Eating diet rich in calcium, phosphates
- Eating hard food
- Use teeth for the proper function
List two dental diseases. (2mks)
- Dental carries
- Periodontal disease.
Define the following terms. (3mks)
Ingestion
Introduction of food into mouth
Digestion
Breakdown of complex food substances into simple soluble substances that can be absorbed into the body
Egestion
Removal of undigested and indigestible food materials from the **.
Name two salivary glands in humans. (2mks)
- Sublingual salivary glands
- Sub-mandibular salivary glands
- Parotid salivary glands
ii) State two functions of saliva. (2mks)
- Contains salivary amylase that digest starch
- Saliva is alkaline that provides optimum PH for enzyme.
- Has mucus that lubricates food hence smooth flow.
Name two nutrients that are absorbed without being digested by enzymes in humans.(2mks)
- Water
- Vitamins
- Mineral salts.
State the functions of the following enzymes (4mks)
- Salivary amylase
- Digest starch to maltose
- Pepsin
- Digest proteins to peptides
- Rennin
- Digest protein caseinogens to casein
- Pancreatic lipase
- Digest lipids to fatty acids and glycerol.
State two functions of hydrochloric acid produced at the stomach. (2mks)
Provides acidic medium optimum for enzyme in the stomach.
State two functions of the bile juice in the digestion of food. (2mks)
- Neutralizes acidic chyme
- Emulsifies fats/lipids
- Provides alkaline medium
List four adaptations of ileum to its functions. (4mks)
- Long to provide large surface area absorption
- Narrow to bring digested food into close contact
- Highly coiled to slow down movement of chyle to allow more time for absorption.
- Inner surface has villi & micro-villi to increase surface area of contact for absorption.
- Thin layer of cells through which digested food diffuses.
| Virus-free.www.avast.com |